
Rheumatoid Lung
© Copyright William Herring, MD, FACR

Rheumatoid Lung
Extra-articular manifestations morecommon in males
Disease more common in females
Clinically
Shortness of breath most common
Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules oftenpresent
PFTs show restrictive disease

Rheumatoid LungGeneral
Most patients with pulmonary evidenceof RA have
Clinical evidence of the disease
Severe arthritic disease

Circulating antibody
Largely IgM in patients with RA
Changes in lung probably immune inorigin
Rheumatoid LungCause

Pleural effusion
Pulmonary fibrosis
Necrobiotic nodules
Caplan’s Syndrome
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Obliterative Bronchiolitis
Rheumatoid LungManifestations

Most common manifestation ofRA in chest
Rheumatoid LungPleural Effusion

Pleural EffusionCharacteristics
Exudate
Very low sugar content (< 30 mg/100 ml)
Does not rise with IV administration ofglucose
Low sugar effusion in TB rises with IVglucose

Pleural fluid in RA
High in LDH
Rich in lymphocytes
Positive for Rheumatoid Factor
Contains low complement levels
Pleural EffusionCharacteristics

Effusion may remain unchanged formonths or years
Most are unilateral
Can occur on either side
Effusion almost never associated withparenchymal disease
Pleural EffusionCharacteristics


Pleural Effusions in RA

Begins micronodular coarse reticulation
More prominent at bases
Indistinguishable from scleroderma
Honeycomb appearance
Rheumatoid LungPulmonary Fibrosis

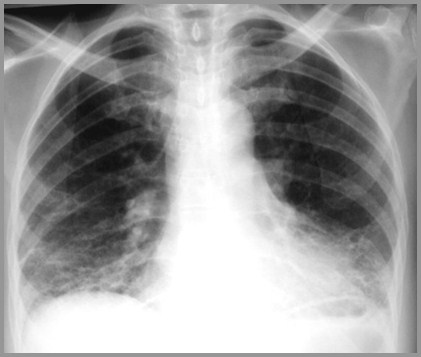
Bibasilar Interstitial Disease in RA

Relatively rare
Usually occur with subcutaneous nodules
Identical pathologically to them
Usually well circumscribed masses
Typically multiple
Subpleural in location with cavitation
Frequently at bases
Rheumatoid LungNecrobiotic Nodules

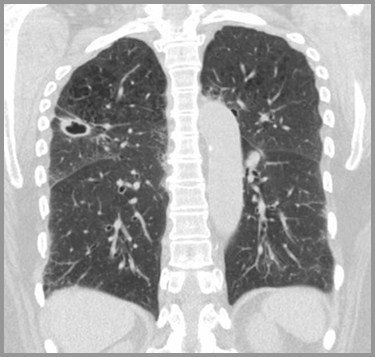
Necrobiotic Nodule in RA

Necrobiotic nodules with silicosis
Pathologically, only difference is ringof dust in nodule which producesdarkened ring around central core
Roentgenographically identical torheumatoid nodules in RA
Rheumatoid LungCaplan’s Syndrome

Rheumatoid Disease with PulmonaryArterial Hypertension
Due to an arteritis which produces PAHand eventual cor pulmonale
Rheumatoid LungPulmonary Hypertension

Same as BOOP except patients have RA
Rheumatoid LungBOOP

The End